Introduction
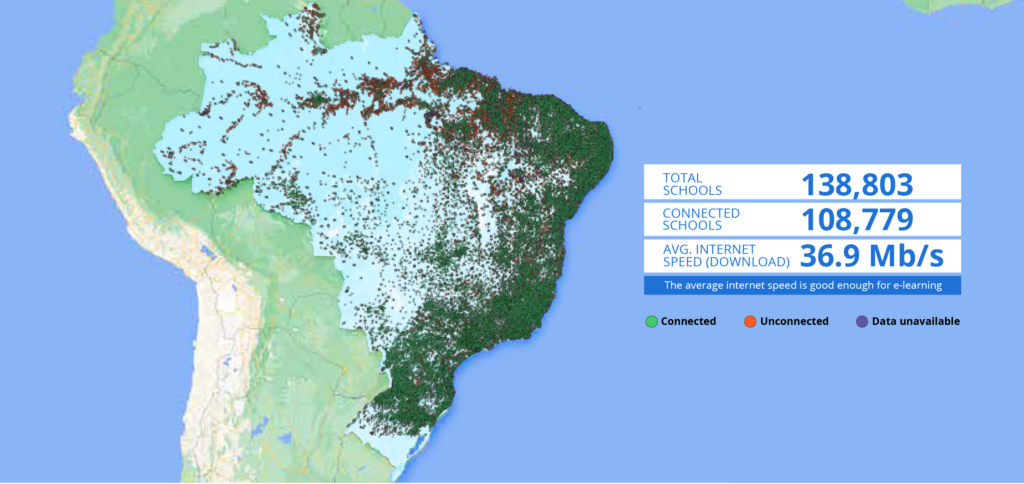
Radio frequency spectrum is a finite public resource that has a wide range of use cases for broadband communications providers and other actors. In recent years, governments have made intentional decisions about spectrum allocations to maximize the economic and social benefits of the resource. By way of auction mechanics, governments introduced additional obligations to auction participants to produce targeted results. While these obligations have an impact on the market value of the licenses, as they often pose a financial burden on the winning bidder, they also transfer responsibility and risk to the entities most capable of delivering certain public goods. In the case of Brazil’s 2021 5G spectrum auction, the auction had no discretionary revenue objective. Rather, the entirety of the proceeds was earmarked for reinvestment in the country’s infrastructure, including school connectivity.
Giga’s founding partner, the International Telecommunication Union (“ITU”) served as an advisor to the Brazilian government in the leadup to the country’s 5G auction. Giga will support the government in several key capacities as the country deploys auction proceeds and connects currently unconnected schools to the internet for the first time.