Internet access is critical for education. Having it means access to information and all the opportunities that information brings – from exposure to new ways of learning to engaging with the world beyond one’s own community. Furthermore, gaining experience with digital tools in and of itself is powerful, which expands economic opportunity, especially for those living in the Global South.
The COVID-19 pandemic threw the importance of digital connectivity into sharp focus, as millions of students were suddenly forced to rely on remote learning. However, reliable access to the Internet is far from a guarantee for many – today 1.3 billion school-aged children don’t have access to the Internet at home, with schools often failing to bridge the gap.
Giga, a joint initiative by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and International Telecommunication Union (ITU), is working in partnership with organizations like Meta to connect all schools to the Internet, and every young person to information, opportunity, and choice.
How Giga Connects Schools to the Internet
Connecting schools to the Internet is a multifaceted problem. In addition to the associated infrastructural and cost challenges, there are also massive data gaps. Basic information – like knowing where schools are and whether they already have Internet access – is often unknown. Giga is working to address these data gaps by mapping the locations of schools, determining whether they have access to the Internet, and if they do, whether the connectivity is strong and stable enough to be effective. Giga also evaluates the availability of infrastructure near schools to determine the options for providing Internet access. This is essential to help governments and connectivity providers understand the costs for connecting schools to the Internet, enabling them to optimize their budget and resources.
Leveraging Meta’s Data to Achieve Connectivity
In order to support Giga’s work, the Data for Good at Meta team shared insights to help the Giga team understand the connectivity infrastructure already available – specifically, the strength of existing cellular networks at school locations, providing estimates on the extent to which 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile coverage exists in the area around each school. This data helps the Giga team evaluate what technologies are already available near a given school and what steps may need to be taken in order to ensure the school has reliable access to the Internet.
Coverage Maps
Using the data on mobile coverage provided by Meta, Giga was able to map Internet coverage for over 500,000 school locations across 37 countries across Asia, South America, and Africa, which are made available to the public on its open-source school mapping platform, Project Connect.
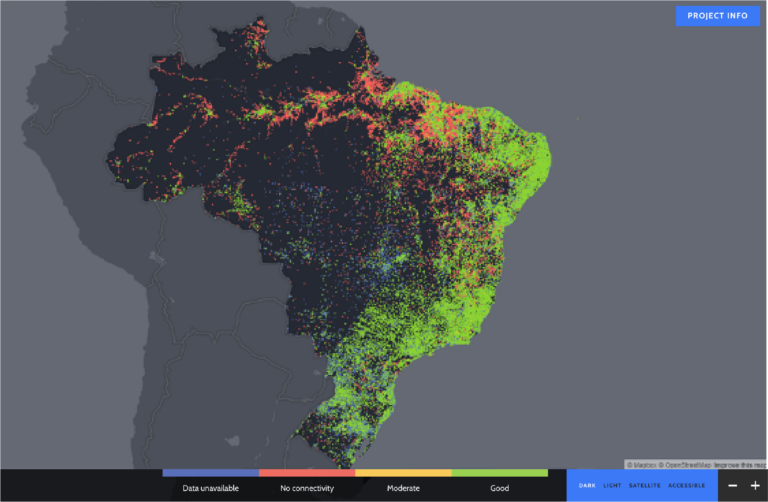
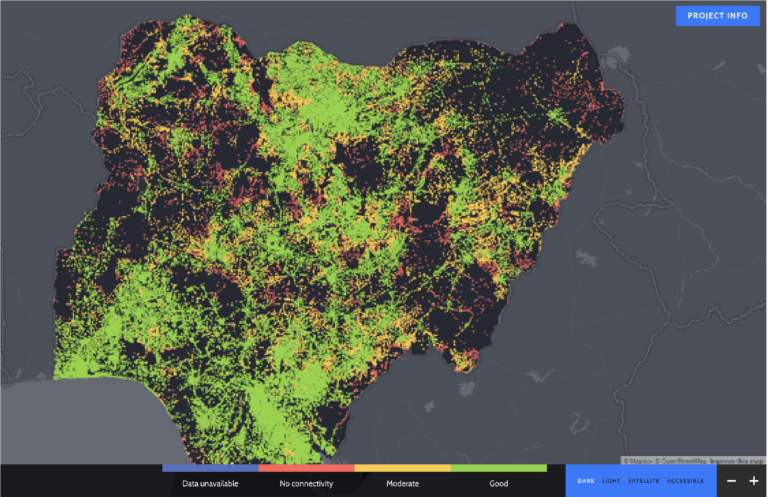
These coverage maps provide insights on the actual coverage situation at various school locations. Moving forward, the dataset provided by Meta will be used by the team for other applications including connectivity cost modelling, infrastructure analysis, and decision support.
By the end of 2022, 2.12 million children in more than 5,500 schools were connected to the Internet through Giga.
But with around half of the world’s 6 to 7 million schools still offline, there is still much work that needs to be done. Giga continues to work on building maps that capture the location of schools, their connectivity status, and other important infrastructure. With this information, Giga hopes to ensure that all schools have sustainable and reliable access to the Internet by 2030.
This piece was written by Giga and the Meta Data for Good Team.

